Cpu z – CPU-Z: Ever wondered what’s really powering your computer? This little utility is your key to unlocking the secrets hidden within your hardware. It’s a free, easy-to-use program that provides detailed information about your CPU, RAM, motherboard, and more, all presented in a clear and understandable format. Whether you’re a seasoned techie or a curious newcomer, CPU-Z offers a fascinating glimpse into the inner workings of your PC.
From identifying your processor’s architecture and clock speed to revealing the specifics of your RAM modules, CPU-Z provides a comprehensive overview of your system’s components. This information is invaluable for troubleshooting, understanding performance, and even considering upgrades. We’ll explore how to use CPU-Z effectively, interpret its data, and uncover some of its more advanced features.
CPU-Z Functionality Overview
CPU-Z is a freeware utility that provides detailed information about your computer’s hardware components. It’s a valuable tool for identifying CPU specifications, RAM details, and motherboard information. Its simple interface makes it accessible to both novice and experienced users.
Core Functions of CPU-Z
CPU-Z’s core functionality centers around identifying and displaying detailed specifications of key hardware components. This includes the CPU, its cache levels, the motherboard chipset, and the installed RAM. It achieves this through direct access to system hardware registers and data structures.
CPU Component Identification
CPU-Z identifies CPU components by accessing specific registers within the CPU itself. This process provides detailed information such as the manufacturer, model, core count, clock speed, and cache sizes. The software then cross-references this data with its internal database to display the most accurate information possible.
Information Displayed for Different CPU Architectures
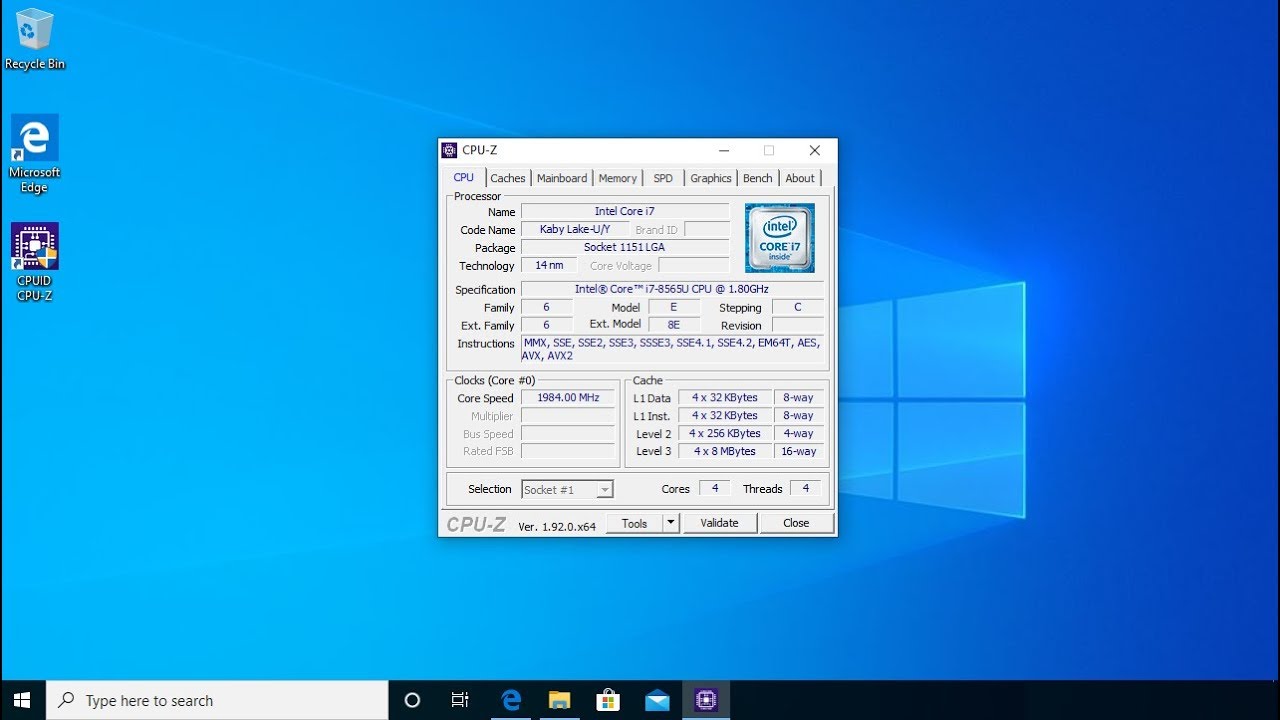
CPU-Z supports a wide range of CPU architectures, including x86 (Intel and AMD), ARM, and others. While the specific details displayed may vary slightly depending on the architecture, the core information (manufacturer, model, clock speed, etc.) remains consistent. For x86 architectures, it provides detailed information about instruction sets, extensions, and other technical specifications. For ARM architectures, the information will be tailored to the specific ARM core being used.
Identifying System RAM Specifications Using CPU-Z
Identifying your system’s RAM specifications with CPU-Z is straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Download and install CPU-Z.
- Open the CPU-Z application.
- Click on the “Memory” tab.
- The “Memory” tab displays detailed information about your RAM, including type, size, speed, and timings.
Below is an example of the data displayed:
| RAM Type | Size | Speed | Timings |
|---|---|---|---|
| DDR4 | 16 GB | 3200 MHz | 16-18-18-38 |
| DDR3 | 8 GB | 1600 MHz | 9-9-9-24 |
| LPDDR4X | 8 GB | 4266 MHz | 15-15-15-36 |
| DDR5 | 32 GB | 5600 MHz | 36-36-36-72 |
CPU-Z and Benchmarking: Cpu Z
While CPU-Z is not a benchmarking tool in the same vein as dedicated applications like Cinebench or 3DMark, it provides valuable data that can be used to understand performance relative to specifications.
Comparison with Other System Information Tools
Compared to other system information tools, CPU-Z stands out for its detailed and specific hardware information. Tools like System Information (Windows) or System Profiler (macOS) offer a broader overview, but CPU-Z delves deeper into the specifics of each component, particularly the CPU and RAM.
Limitations for Detailed Performance Analysis
CPU-Z’s primary focus is hardware identification, not performance measurement. It doesn’t provide metrics like frame rates, benchmark scores, or detailed CPU utilization graphs. For comprehensive performance analysis, dedicated benchmarking software is necessary.
Understanding CPU Performance Relative to Specifications
CPU-Z provides the baseline specifications (clock speed, core count, cache size) against which you can compare observed performance. If your CPU is consistently running below its specified clock speed, it could indicate an issue with power delivery, cooling, or driver problems.
Interpreting CPU Clock Speeds and Multiplier Values
CPU-Z displays both the current clock speed and the multiplier value. The multiplier is a factor that multiplies the base clock speed to determine the final CPU clock speed. For example, a base clock of 100 MHz and a multiplier of 40 results in a clock speed of 4 GHz. Deviations from expected values can indicate throttling or overclocking.
So you’re checking your CPU specs with CPU-Z, right? It’s a great tool for that kind of thing. Thinking about the future of logistics though, have you considered the potential impact of companies involved in drone delivery Canada stock ? It’s a rapidly growing sector, and the processing power needed for drone control systems is seriously impressive – stuff that would make even a high-end CPU sweat! Back to CPU-Z though, it’s still useful for monitoring your current system’s performance.
CPU-Z and Troubleshooting
CPU-Z can be a valuable tool for diagnosing various hardware-related problems. By examining the reported information, you can often pinpoint the source of an issue.
Diagnosing Potential Issues Using CPU-Z
CPU-Z can help identify problems such as incorrect RAM speed, compatibility issues between CPU and motherboard, and potential overclocking instability. It can also reveal if the CPU is correctly identified by the system, which can help diagnose boot problems.
Detecting Overclocked CPUs
By comparing the reported clock speed in CPU-Z to the CPU’s specifications, you can easily determine if it’s been overclocked. A clock speed significantly higher than the rated speed indicates overclocking. This can be useful for verifying successful overclocking or detecting unexpected overclocking attempts.
Checking for CPU and Motherboard Compatibility
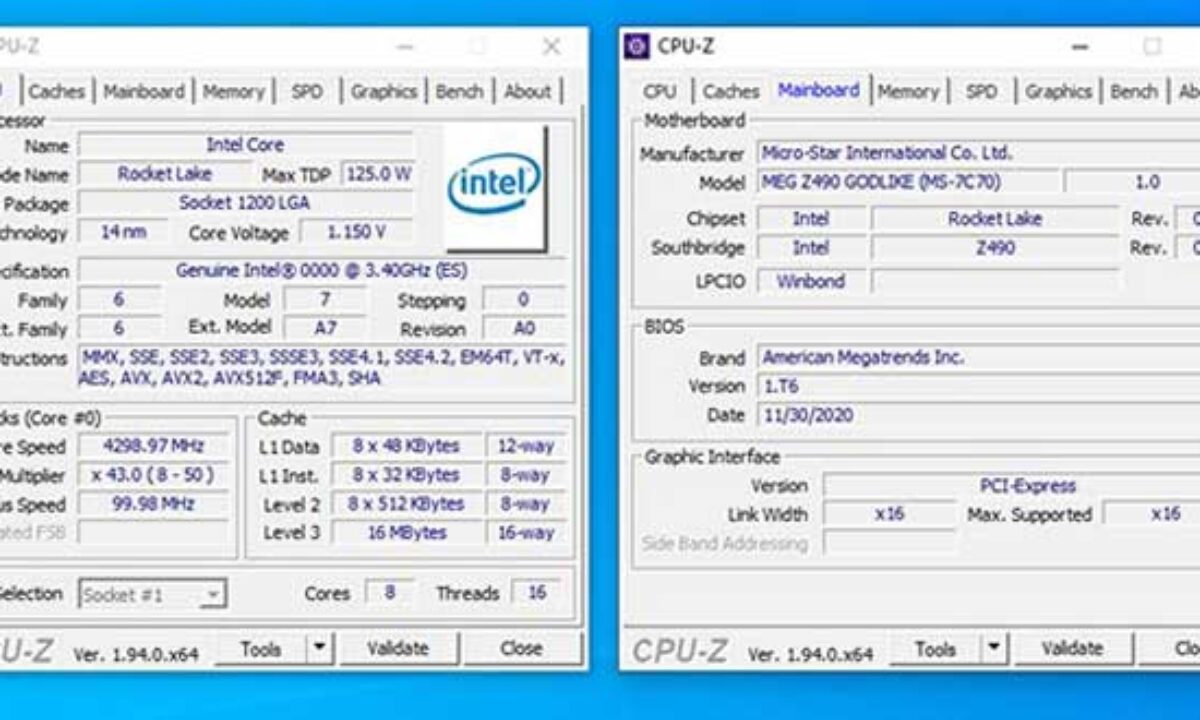
CPU-Z displays the CPU socket type and the motherboard chipset. By comparing this information with the specifications of your CPU and motherboard, you can verify compatibility. Discrepancies might indicate a compatibility issue.
Examples of CPU-Z Error Messages and Their Causes
- “CPU not detected”: This could be due to a faulty CPU, a problem with the CPU socket, or a BIOS issue.
- “Memory not detected”: This usually points to faulty RAM modules, incorrect RAM configuration, or a problem with the memory controller.
- “Incorrect CPU speed”: This can be caused by incorrect BIOS settings, driver issues, or a problem with the CPU itself.
CPU-Z Data Visualization
While CPU-Z doesn’t offer built-in visualization, the data it provides can be easily used to create informative charts and diagrams.
Visual Representation of CPU Core Information
A bar chart would be ideal for representing CPU core information. Each bar could represent a core, with the height corresponding to the core’s clock speed. This provides a clear visual comparison of the clock speeds across different cores.
Visual Representation of CPU Cache Levels and Sizes, Cpu z
A nested pie chart could effectively visualize CPU cache levels and sizes. The main pie chart represents the total cache size, with slices representing different cache levels (L1, L2, L3). Each slice can then be further subdivided to show the sizes of the individual cache levels.
Visual Representation of CPU Temperature
A line graph is suitable for displaying CPU temperature over time. The x-axis represents time, and the y-axis represents temperature. This allows users to monitor temperature fluctuations and identify potential overheating issues. The intended audience is users who want to monitor their CPU’s thermal performance.
CPU-Z’s Use in Different Operating Systems
CPU-Z is available for Windows, Linux, and macOS. While the core functionality remains consistent across platforms, there might be minor differences in the interface and the specific information displayed.
Information Displayed Across Different Operating Systems
The fundamental information provided by CPU-Z (CPU model, RAM specifications, motherboard details) remains largely consistent across Windows, Linux, and macOS. However, the presentation might differ slightly, reflecting the UI conventions of each operating system.
Differences in Functionality or Interface
The interface might vary slightly between operating systems to align with the platform’s design guidelines. The specific details reported might also vary depending on the operating system’s ability to access certain hardware information.
Installing CPU-Z on a Linux System
The installation process on Linux typically involves downloading the appropriate package (usually a .tar.gz archive) from the CPU-Z website. Extract the archive, navigate to the extracted directory, and run the executable. Some distributions may offer CPU-Z packages through their package managers.
Advanced CPU-Z Features
Beyond the basic information, CPU-Z offers access to more advanced features that are useful for experienced users.
Features Related to Memory Controllers
CPU-Z provides details about the memory controller integrated into the CPU. This includes information about the memory channels, the type of memory supported, and other related specifications. This is crucial for understanding memory performance and potential bottlenecks.
Advanced Features Related to Chipsets or Motherboard Technologies
CPU-Z often displays detailed information about the motherboard chipset, including its manufacturer, model, and specific features. This information can be valuable for troubleshooting and understanding the capabilities of the motherboard.
Interpreting Technical Information in CPU-Z
- Stepping: This refers to a specific revision of a CPU model. Different steppings might have bug fixes or minor performance improvements.
- Revision: This indicates the manufacturing revision of a component, similar to stepping but often broader in scope.
Closure

CPU-Z is more than just a system information tool; it’s a window into the heart of your computer. By understanding how to use its features and interpret its data, you gain a deeper appreciation for your system’s capabilities and limitations. Whether you’re troubleshooting a problem, planning an upgrade, or simply satisfying your curiosity, CPU-Z is a powerful and readily accessible resource.
So, download it, explore its features, and discover the hidden potential within your own machine!
FAQ Section
Is CPU-Z safe to use?
CPU-Z is a great tool for checking your system specs, especially if you’re troubleshooting performance issues. Sometimes, though, slowdowns might not be hardware-related; you might find yourself wondering, “Is chatgpt down? ,” because a slow AI could be impacting your workflow. Once you’ve ruled out that possibility, though, you can get back to using CPU-Z to pinpoint the actual source of the problem on your machine.
Yes, CPU-Z is a safe and reputable program from a well-known developer. It’s a lightweight application that doesn’t require extensive permissions.
Can CPU-Z damage my computer?
No, CPU-Z is purely a read-only tool. It doesn’t modify any system settings or hardware components.
CPU-Z is a great tool for checking your system specs, especially if you’re troubleshooting performance issues. Sometimes, though, a slow computer isn’t hardware related; you might find that the problem stems from a service outage like checking if chat gpt down is affecting your workflow. Once you’ve ruled out external issues, CPU-Z can help pinpoint bottlenecks within your system itself.
What if CPU-Z shows incorrect information?
Incorrect information is rare but could be due to driver issues or hardware problems. Try updating drivers or checking for hardware malfunctions.
Where can I download CPU-Z?
Download CPU-Z directly from the official CPUID website to ensure you get the legitimate and virus-free version.
