How to operate a drone? This guide delves into the exciting world of unmanned aerial vehicles, providing a comprehensive overview of everything from fundamental flight controls to advanced techniques and essential safety protocols. We’ll explore the legal landscape surrounding drone operation, ensuring you fly responsibly and within the bounds of the law. From selecting the right drone for your needs to mastering complex maneuvers, this guide serves as your complete handbook for safe and successful drone piloting.
Understanding drone operation goes beyond simply mastering the controls; it involves a deep understanding of airspace regulations, safety procedures, and responsible piloting practices. This guide equips you with the knowledge to confidently navigate the skies, capture stunning aerial footage, and contribute to the responsible growth of the drone industry. We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks to maintenance and troubleshooting, making sure you’re prepared for any situation.
Drone Regulations and Safety: How To Operate A Drone

Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local regulations and prioritizing safety. Failure to do so can result in accidents, fines, and legal repercussions. This section covers essential safety procedures and legal considerations for safe drone operation.
Legal Requirements for Drone Operation
Drone laws vary significantly by location. National parks often have strict regulations, potentially prohibiting drone flights altogether or restricting them to designated areas. Urban areas usually have airspace restrictions near airports and other sensitive infrastructure. Before flying, always check the specific regulations for your location using resources like the FAA website (for the USA) or equivalent agencies in other countries.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning to navigate safely and effectively is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Ultimately, responsible operation ensures both the safety of your drone and those around you.
Register your drone with the appropriate authorities as required.
Drone Flight Safety Procedures
Safe drone operation involves a multi-stage process encompassing pre-flight checks, in-flight awareness, and post-flight procedures. Neglecting any of these steps increases the risk of accidents.
- Pre-flight: Conduct a thorough pre-flight inspection (detailed in the next section), check weather conditions (avoid strong winds or rain), and ensure you have the necessary permissions for your flight location.
- In-flight: Maintain visual line of sight with your drone at all times, avoid flying near people or obstacles, and be aware of your surroundings. Respect the privacy of others and avoid flying over private property without permission.
- Post-flight: Inspect your drone for any damage, securely store the drone and its components, and review your flight data to identify any potential issues.
Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist
A comprehensive pre-flight checklist is crucial for safe operation. This ensures all systems are functioning correctly and reduces the risk of malfunctions during flight.
- Check battery levels and ensure they are fully charged.
- Inspect propellers for damage or wear.
- Verify GPS signal strength.
- Test all control functions on the transmitter.
- Confirm camera functionality (if applicable).
- Review weather conditions and ensure they are suitable for flight.
Common Drone Accidents and Avoidance
Common drone accidents often stem from pilot error, equipment malfunction, or environmental factors. Understanding these risks allows for proactive mitigation.
- Loss of signal: Maintain a close proximity to the drone and avoid obstacles that might interfere with the signal. Consider using a signal booster.
- Collisions: Always maintain visual line of sight and be aware of your surroundings. Avoid flying in crowded areas.
- Battery failure: Use high-quality batteries and monitor their charge levels closely. Always have a spare battery available.
- Mechanical failure: Regularly inspect your drone for damage and perform maintenance as needed.
Airspace Restrictions
Understanding airspace restrictions is vital for legal and safe drone operation. These restrictions vary depending on location and proximity to airports, military bases, and other sensitive areas.
| Airspace Class | Description | Restrictions | Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class A | Highest altitude airspace, typically above 18,000 feet | Requires special authorization | Generally inaccessible to recreational drones |
| Class B | Surrounds major airports | Strict regulations and authorization required | Drone operation highly restricted or prohibited |
| Class G | Uncontrolled airspace | Generally open to drone operation, but with other regulations | Requires adherence to all other applicable rules and regulations |
| Special Use Airspace | Areas designated for specific purposes (military, wildlife reserves, etc.) | Highly variable restrictions, often prohibiting drone operation | Consult local authorities before operating in these areas |
Choosing and Setting Up Your Drone
Selecting the right drone and properly setting it up are crucial steps for a successful flying experience. Consider your needs and budget when choosing a model, and ensure you understand the setup process before your first flight.
Drone Model Comparison
Drone models cater to various needs and budgets, from basic recreational models to advanced professional-grade systems. Photography and videography drones emphasize camera quality and stabilization, while racing drones prioritize speed and maneuverability.
- Photography/Videography: Look for features like high-resolution cameras, image stabilization, and intelligent flight modes.
- Racing: Prioritize lightweight design, powerful motors, and agile responsiveness.
- Recreational: Focus on ease of use, durability, and a balance of features and price.
Charging and Calibrating the Battery
Proper battery care is essential for safe and reliable drone operation. Always use the manufacturer’s recommended charger and follow their instructions carefully.
- Use the supplied charger to charge the battery fully.
- Avoid overcharging or discharging the battery.
- Store batteries in a cool, dry place.
- Calibrate the battery using the drone’s software or app as instructed by the manufacturer (this step may vary depending on the drone model).
Setting Up the Drone Controller
Connecting the controller to the drone is a straightforward process, but it’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions precisely. Most drones use a 2.4 GHz or 5.8 GHz frequency for communication.
- Turn on the drone and the controller.
- Bind the controller to the drone (the specific process varies by model; consult the manual).
- Calibrate the controller sticks (usually involves moving the sticks to their extremes and centering them).
- Check the connection by attempting to control the drone’s motors (in a safe, open area).
Selecting Appropriate Propellers
Propellers significantly influence flight performance. Choosing the correct propellers is essential for optimal efficiency, stability, and safety.
- Larger propellers generate more thrust but reduce flight time.
- Smaller propellers provide better maneuverability and longer flight times but with less lifting power.
- Always use propellers that are specifically designed for your drone model.
Essential Drone Accessories
Several accessories enhance drone operation and safety. Investing in these can significantly improve your flying experience.
- Extra batteries
- Spare propellers
- Carrying case
- Propeller guards (for added safety)
- Smartphone mount (if your controller doesn’t have a built-in screen)
Basic Drone Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is fundamental to safe and enjoyable drone operation. This section details essential maneuvers and control techniques.
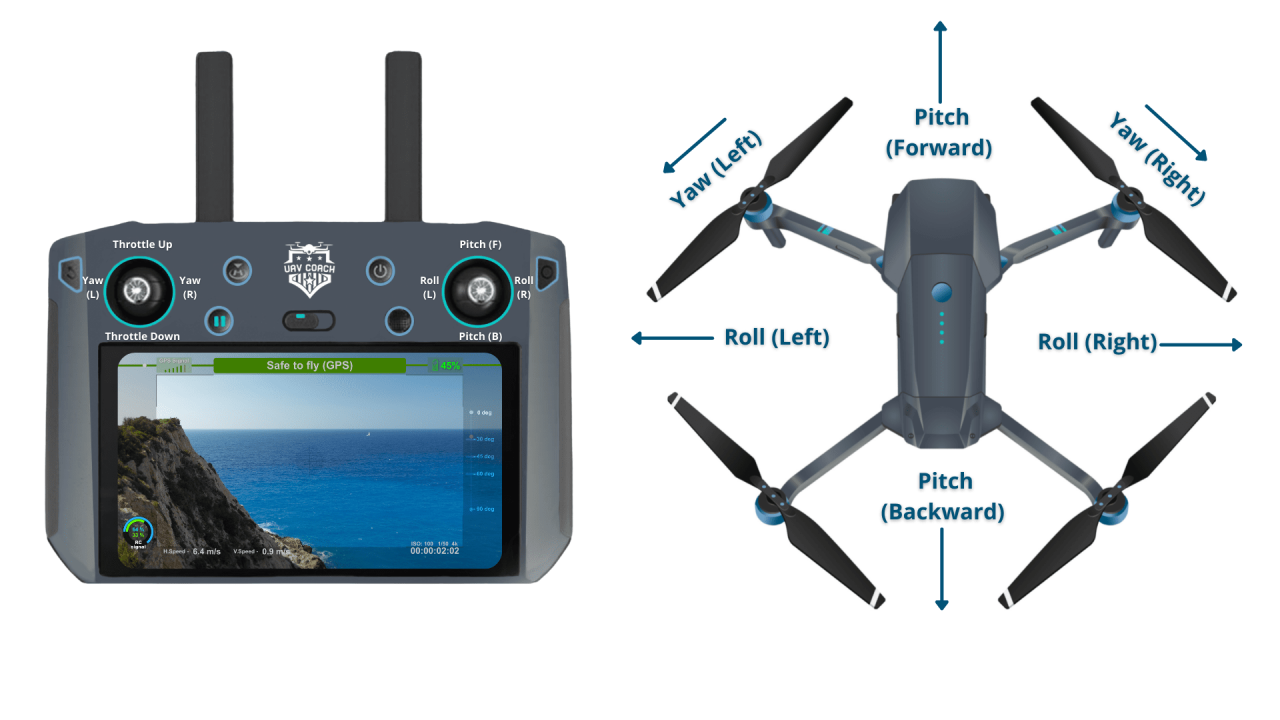
Drone Controller Functions
Most drone controllers use two joysticks to control the drone’s movement. One joystick typically controls altitude and direction, while the other controls yaw (rotation) and movement along the horizontal plane.
- Left Stick (typically): Controls altitude (up/down) and forward/backward movement.
- Right Stick (typically): Controls yaw (rotation) and left/right movement.
- Buttons: Buttons on the controller typically control functions like camera operation, Return-to-Home (RTH), and emergency stops.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
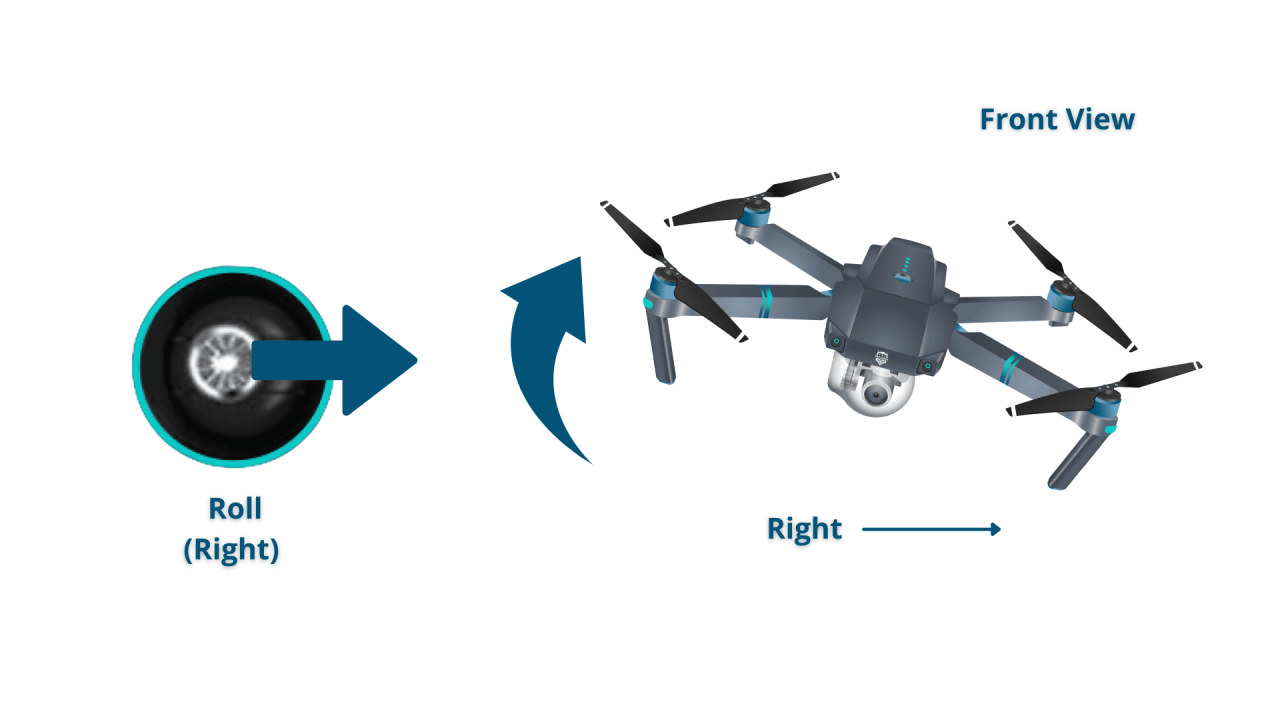
Mastering basic maneuvers is crucial before attempting more complex flights. Practice these in a safe, open area away from obstacles.
- Takeoff: Gently push the left stick upwards to initiate takeoff.
- Landing: Gently push the left stick downwards to initiate landing.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air by carefully adjusting the left stick.
- Movement: Use the left and right sticks to move the drone in different directions.
Altitude and Stability Control
Maintaining stable altitude and smooth movements are key to safe and effective drone operation. Practice using the left stick to make small adjustments to maintain a constant altitude.
- Use the left stick gently to control altitude. Avoid abrupt movements.
- Use the drone’s stability features (if available) to assist in maintaining a stable flight.
- Practice hovering in different wind conditions to gain experience.
Tips for Smooth Drone Movements

Smooth and controlled movements are essential for capturing high-quality photos and videos. Avoid jerky movements, and use the drone’s features to assist in maintaining a steady flight path.
- Use small, gradual movements of the control sticks.
- Practice slow and controlled maneuvers before attempting more complex flights.
- Utilize the drone’s intelligent flight modes (if available) to assist with stabilization and automated maneuvers.
Flying in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions requires additional skill and caution. Adjust your flying technique to compensate for wind gusts.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers, I highly recommend checking out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills will allow you to confidently and safely enjoy the exciting world of drone piloting, ensuring both your safety and the safety of those around you.
Ultimately, responsible operation is key to a positive drone experience.
- Assess wind speed and direction before attempting flight.
- Fly into the wind during takeoff and landing to gain more control.
- Use small, controlled movements to adjust for wind gusts.
- Be prepared to land immediately if wind conditions become unsafe.
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques
Advanced flight techniques unlock the drone’s full potential, enabling complex maneuvers and precise control. This section explores waypoint navigation, GPS utilization, and aerial photography/videography.
Waypoint Navigation and Flight Path Programming
Waypoint navigation allows you to pre-program a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously. This is useful for creating complex shots or surveying large areas.
- Most drones offer waypoint programming through their dedicated mobile apps.
- You can define specific points in space for the drone to fly to in sequence.
- Advanced features may allow for setting speed, altitude, and camera angles at each waypoint.
GPS and Sensor Utilization
GPS and other sensors (such as IMUs and barometers) provide crucial data for precise drone control and stability. They enable features like Return-to-Home (RTH) and allow for more accurate flight path planning.
- GPS provides location data, enabling accurate positioning and autonomous flight.
- IMUs (Inertial Measurement Units) measure the drone’s orientation and movement.
- Barometers measure altitude, contributing to precise altitude control.
Return-to-Home (RTH) Function, How to operate a drone
The Return-to-Home (RTH) function is a critical safety feature that automatically returns the drone to its takeoff point if the signal is lost or the battery is low.
- Ensure that the RTH function is properly calibrated and configured.
- Regularly test the RTH function to ensure it’s working correctly.
- Understand the limitations of the RTH function; it may not be effective in all conditions (e.g., strong winds).
Aerial Photography and Videography Techniques
Capturing high-quality aerial footage requires understanding composition, framing, and camera settings. Practice different angles and perspectives to create dynamic visuals.
- Shot Composition: Use the rule of thirds to create visually appealing images.
- Framing: Experiment with different angles and perspectives to create dynamic shots.
- Camera Settings: Adjust settings like aperture, shutter speed, and ISO to optimize image quality.
Complex Drone Maneuver: Figure-Eight Pattern
Imagine the drone starting at a central point. It moves smoothly forward, then gently curves upwards and to the right, forming half of a circle. At the apex of this curve, it smoothly transitions into a downward curve to the left, completing the top half of the figure eight. It continues this pattern, mirroring the first half on the lower portion, creating a complete, symmetrical figure eight pattern in the air.
The entire maneuver is executed with fluid, continuous movements, maintaining a consistent altitude and speed.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its safe operation. This section Artikels key maintenance tasks and common troubleshooting steps.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
Regular maintenance prevents problems and ensures optimal performance. Develop a maintenance schedule based on your frequency of use.
- Daily: Inspect propellers, body, and camera for damage. Check battery levels.
- Weekly: Clean the drone body and propellers. Check for loose screws or connections.
- Monthly: Conduct a more thorough inspection, checking all components and connections.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Understanding common malfunctions allows for quick diagnosis and resolution. Always consult your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
- No power: Check battery levels, connections, and the drone’s power switch.
- GPS signal loss: Ensure clear skies and a strong GPS signal. Check for obstructions.
- Propeller malfunction: Inspect propellers for damage and replace if necessary.
- Controller issues: Check battery levels, connections, and try re-binding the controller to the drone.
Replacing Damaged Parts
Replacing damaged parts is often straightforward, but it’s essential to use genuine replacement parts to maintain safety and performance. Consult your drone’s manual for instructions.
- Order replacement parts from the manufacturer or a reputable supplier.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully when replacing parts.
- Test the drone thoroughly after replacing any parts.
Proper Drone Storage
Proper storage protects the drone from damage and extends its lifespan. Store it in a cool, dry, and secure location.
- Store the drone in its carrying case or a protective container.
- Keep batteries charged to around 50% for long-term storage.
- Store the drone away from direct sunlight, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
Drone Troubleshooting Flowchart
A flowchart can help systematically diagnose and resolve drone problems. This example provides a simplified overview.
- Problem: Drone won’t power on.
- Check: Battery level. Is it charged?
- Yes: Check battery connections. Are they secure?
- Yes: Check power switch. Is it turned on?
- Yes: Try a different battery. Does it work?
- Yes: Contact manufacturer for support.
- No (at any point): Proceed to the next step.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical experience. This guide has provided a foundational understanding of drone regulations, flight mechanics, and maintenance procedures. Remember, responsible and safe operation is paramount. By adhering to the guidelines Artikeld here and continuing to hone your skills through practice and further learning, you can unlock the full potential of your drone while ensuring both your safety and the safety of others.
The skies await!
Helpful Answers
What is the maximum flight time for most consumer drones?
Flight times vary greatly depending on the drone model and battery, but typically range from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If possible, attempt to engage the Return-to-Home (RTH) function. If RTH fails, immediately contact local authorities and report the incident.
What are the penalties for violating drone regulations?
Penalties can range from fines to drone confiscation and even criminal charges, depending on the severity of the violation and local laws.
